
Newsroom
A session is hosted to further explain the scientific advances of 2024 in China released at the opening ceremony of the 2025 Zhongguancun Forum, Beijing, China, March 27, 2025. /CGTN's Guo Meiping
The 2025 Zhongguancun Forum (ZGC Forum) kicked off in Beijing on Thursday. At the opening ceremony, China's 10 scientific advances of 2024 were released.
The selection of the advances is hosted by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) and organized by the High Technology Research and Development Center (Basic Research Management Center) of NSFC.
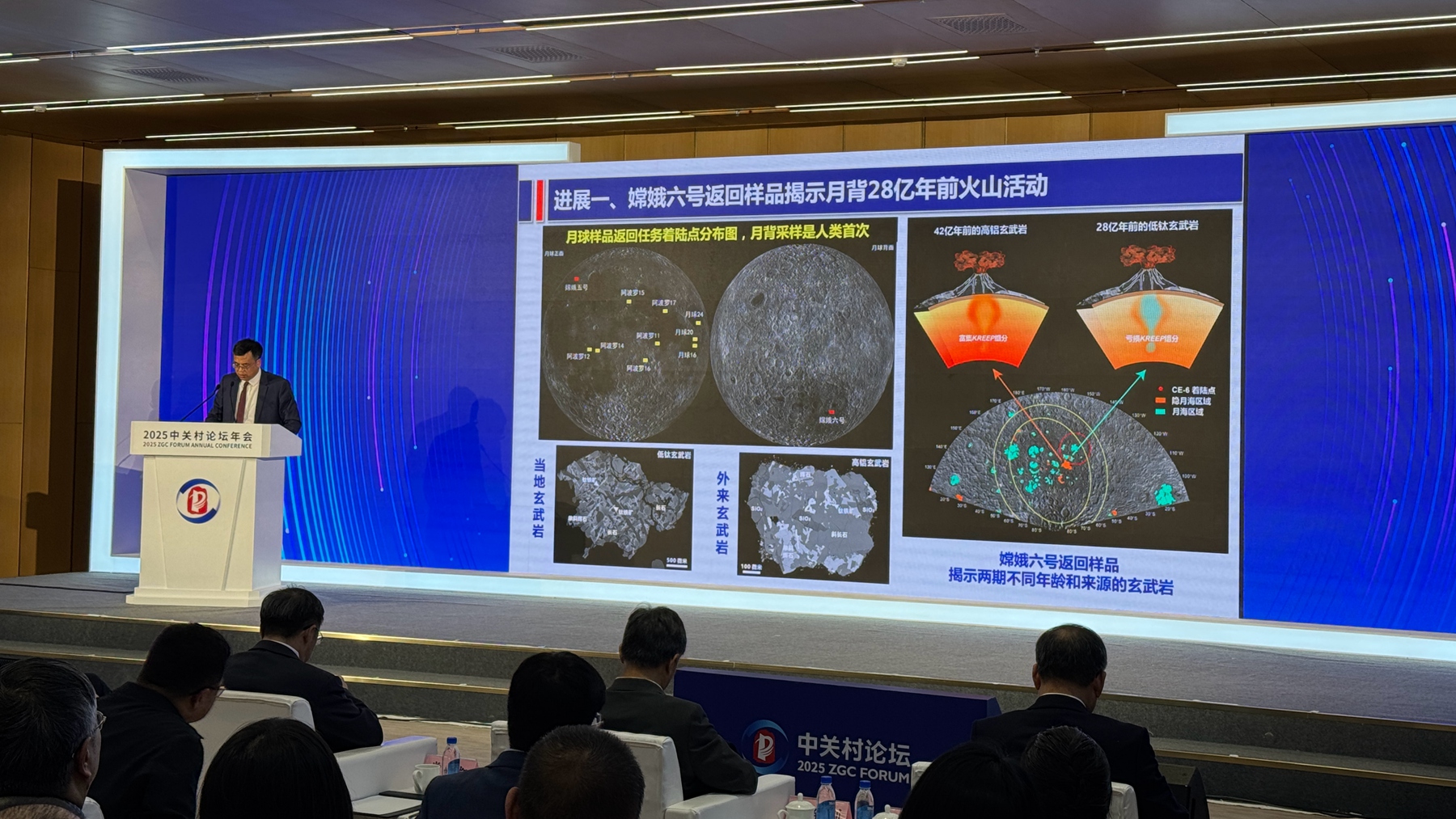
1. Samples returned by the Chang'e-6 mission reveal lunar far side volcanism 2.8 billion years ago
Chang'e-6 mission samples reveal volcanic activity on the moon's far side 2.8 billion years ago. Chinese researchers found basalt, breccia, glass, and light-colored rock fragments with low density and bimodal grain size. The basalt's unique composition suggests a complex origin, formed from a depleted mantle source. Evidence also points to volcanic activity 4.2 billion years ago, highlighting a long volcanic history. These samples offer crucial insights into the moon's geological differences, impact history, and volcanic evolution, marking a new era in lunar research.
2. Large-scale photonic chiplets empower the training and inference for artificial general intelligence
Researchers developed the "Taichi" photonic chiplet, achieving 160-Tera Operations per Joule energy efficiency. It introduces a new architecture that enables efficient in-situ photonic training, eliminating reliance on electronic systems. The chiplet boosts energy efficiency by two orders of magnitude and accelerates training speed tenfold. This breakthrough is expected to advance foundation models, artificial general intelligence, and unmanned systems, providing a high-speed, energy-efficient computing path in the post-Moore era.
3. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms of monoamine neurotransmitter transporters and the action of psychiatric drugs
Researchers explored neurotransmitter transporters like DAT, NET, GlyTl, and VMAT2 to uncover the molecular basis of neurotransmitter regulation. Their findings reveal how psychiatric drugs interact with these transporters, identifying new binding sites that reduce addictive risks. This research offers insights for developing safer neuropsychiatric drugs with fewer side effects.
4. Nanolasers with atomic-scale feature sizes and reconfigurable phased arrays
Researchers developed atomic-scale nanolasers using a unique dispersion equation, achieving the smallest mode volumes yet. These nanolasers demonstrated coherent lasing patterns like the Chinese characters "中" and "国" (China), offering powerful imaging tools for materials and life sciences. Their low energy use and fast modulation speeds hold promise for IT and other fields.
5. Discovery of giant magnetocaloric effect in spin supersolid state and new mechanism for ultra-low temperature refrigeration
Researchers discovered a spin supersolid state in a cobalt-based material, combining solid and superfluid traits. This quantum state achieves a giant magnetocaloric effect, enabling ultra-low temperatures of -273.056 degrees Celsius without helium-3. This breakthrough opens new avenues for advanced cryogenic cooling solutions.
6. Allogeneic CAR-T therapy for autoimmune diseases
Researchers successfully treated patients with severe autoimmune diseases using universal CAR-T cells from healthy donors. This marks the first international success in achieving significant clinical efficacy with allogeneic CAR-T cells, improving accessibility and reducing costs.
7. Extra X chromosome impairs the development of male germ cells in multiple dimensions
A study revealed that developmental defects in male germ cells with an extra X chromosome begin in the fetal stage. The failure to inactivate the extra X chromosome disrupts gene regulation, hindering cell differentiation and leading to infertility.
8. Experimental discovery of graviton modes in condensed matter
Researchers observed graviton-like particles in GaAs quantum wells, revealing spin-2 low-energy excitations in the fractional quantum Hall effect. This discovery advances quantum gravity research and enhances understanding of semiconductor structures and topological quantum computing.
9. The creation of high-energy-conversion-efficiency actinide-based radio photovoltaic micronuclear battery
Researchers developed a novel actinide-based micronuclear battery featuring a coalescent energy transducer that boosts energy conversion efficiency 8,000-fold. This battery design achieves record-high efficiency and introduces new strategies for radioactive waste recovery.
10. Discovery of key evidence that supermassive black holes influence the formation and evolution of host galaxies
A study found that galaxies with more massive supermassive black holes (SMBHs) have less cold gas, crucial for star formation. This finding confirms SMBHs' role in transitioning galaxies from active to quiescent states, advancing understanding of galaxy evolution.
Themed "New Quality Productive Forces and Global Technology Cooperation," this year's ZGC forum will run until March 31. (CGTN)
